High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a leading risk factor for heart disease and stroke. While medication is often necessary for managing severe cases, dietary changes can play a significant role in reducing blood pressure naturally. One of the most well-researched and effective dietary strategies for hypertension is the DASH diet — Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension. Alec Kherlopian, MD, a cardiologist supportive of the DASH diet and director of the hypertension clinic at the Heart Institute, provides insight into how it works, its benefits, and why it stands out among other dietary approaches.
How does the DASH Diet Work?
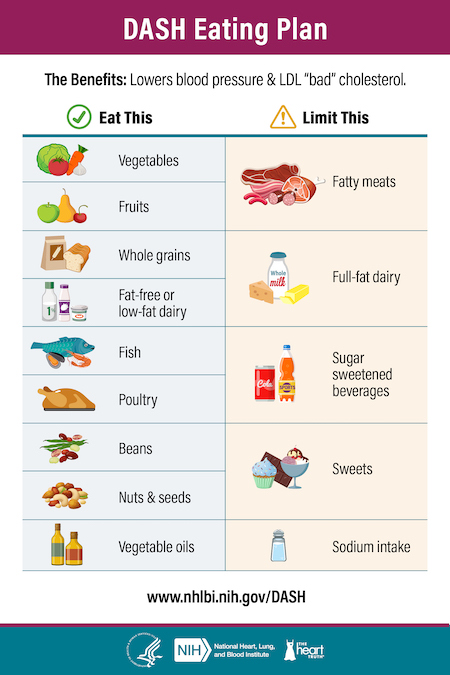
The DASH diet is designed to help lower blood pressure by reducing sodium intake, limiting saturated fat, and promoting nutrient-rich foods known to support heart health.
"One commonly known method blood pressure can increase is through excessive salt intake, which raises blood volume and arterial pressure," Kherlopian says. "The DASH diet encourages a meal plan with limited salt intake, typically between 1,500mg and 2,300mg daily."
Beyond sodium reduction, the DASH diet emphasizes:
- Low intake of saturated fat, which is linked to elevated blood pressure.
- Consumption of fiber-rich foods, whole grains, and legumes.
- Increased intake of vegetables, fruits, and nuts like walnuts, which have been associated with a lower risk of hypertension.

How effective is the DASH Diet?
The DASH diet has consistently ranked as one of the best dietary plans for managing high blood pressure. U.S. News & World Report recently named it the "Best Diet for High Blood Pressure" in 2025.
"Compared to other diets, the DASH diet is effective because it is not as restrictive as very low-carb, paleo, or vegetarian diets," Kherlopian says. "However, effectiveness can vary among individuals. A low-carb diet may result in greater blood pressure reduction for some patients, but the DASH diet is easier to maintain long-term."
DASH Eating Plan to help with your new lifestyle.
Additional health benefits
Beyond lowering blood pressure, adhering to the DASH diet has several additional health benefits:
- Reduction in LDL ('bad') cholesterol levels.
- Lower Hemoglobin A1c, which is beneficial for blood sugar control.
- Weight loss, which further supports heart health.
- Reduced risk of stroke and coronary artery disease, as shown in outcome-based trials.
People with certain health conditions may need to modify the standard DASH diet. For example:
- Diabetes: A lower carbohydrate version of the DASH diet may be more effective in controlling blood sugar levels.
- Kidney Disease: Patients should limit potassium-rich foods to prevent excess potassium buildup in the body.
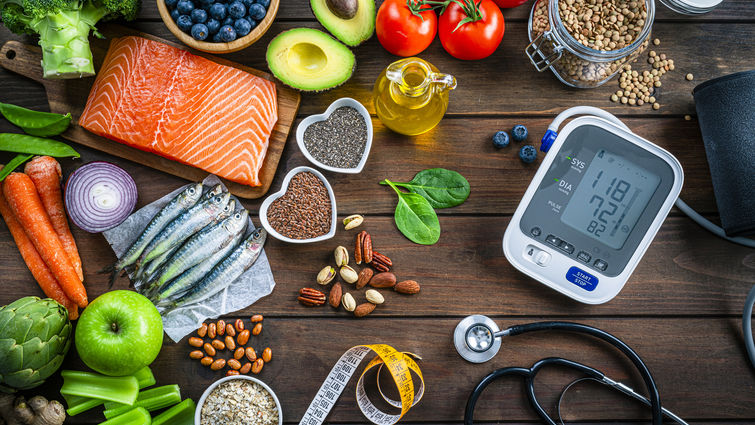
Key foods for lowering blood pressure
While no single food is a "magic bullet" for reducing hypertension, research supports the benefits of incorporating:
- Walnuts – 42.5g per day
- Fruits – Grapes, raisins, apples, pears, and blueberries (100g per day)
- Vegetables – Broccoli, carrots, and avocado (100g per day)
- Dietary Fiber – 28g per day for women, 38g per day for men
Kherlopian strongly recommends the DASH diet as a primary intervention for managing high blood pressure. "It is flexible, effective, and widely supported by credible resources to help patients create meal plans that adhere to its guidelines."
When diet alone isn’t enough
While the DASH diet is a powerful tool for managing hypertension, some individuals may still require medication. "If blood pressure reduction is not achieved through dietary changes alone, antihypertensive medication may be necessary," Kherlopian says. "Additionally, other herbal and nutritional supplements may help and should be discussed with a healthcare provider."
The DASH diet is a well-balanced, scientifically supported approach to lowering blood pressure and improving overall heart health. By incorporating whole foods, reducing sodium, and maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing hypertension and reducing their risk of cardiovascular disease.
Want to learn more about heart health? Take the next step, learn heart healthy recipes, and find expert advice here.