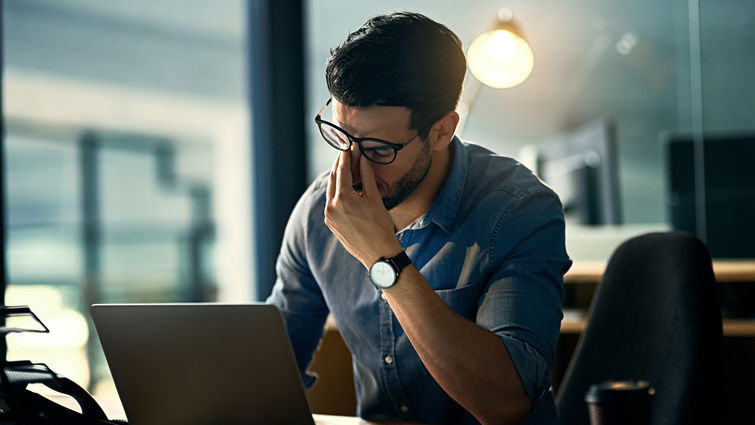
As the stigma against mental health continues to decrease, more adults are seeking evaluation when they think they might have a psychiatric disorder. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is the most common neurodevelopmental disorder in children and it often persists into adulthood. Many adults remain undiagnosed according to Jennifer Minami, MD, a psychiatrist at Loma Linda University Behavioral Health. Receiving a new diagnosis of adult ADHD can be overwhelming, but it can be managed successfully with the right support and information.
ADHD is a complex brain-based disorder that manifests in people’s lives by creating difficulty with focusing on tasks, easily feeling restless, and managing their time. Additionally, they may struggle with organization, forgetfulness, and experience trouble following instructions or conversations without getting distracted.
“While a full understanding of ADHD’s causes is not clear, we do know it is a highly heritable condition, meaning that there is a significant genetic component to its cause,” Minami says.
Not only do individuals with ADHD function differently, but Minami also says there are structural differences in the brain compared to those without ADHD.
“The prefrontal cortex, responsible for many important brain functions, can be impaired in individuals with ADHD. Some essential functions include organization, impulse control, and time management,” Minami says.
Challenges specific to ADHD in adulthood
Poor time management and concentration, forgetfulness, and procrastination are a few symptoms that impact an adult's work or higher education performance. Studies show adults with ADHD are more likely to face difficulty gaining and maintaining employment compared to neurotypical adults, especially if they did not receive treatment in childhood.
“In clinical practice, I will often evaluate individuals with undiagnosed ADHD who have come to label themselves as ‘lazy,’ constantly frustrated by a feeling of underachievement and lifelong pattern of procrastination,” Minami says.
Other symptoms associated with ADHD, like low frustration tolerance, impulsivity, and speaking out of turn, can cause strain on relationships. According to Minami, the first component of treatment is education for the individual diagnosed and the significant individuals in their lives, such as partners or people they live with. She says educating all parties on ADHD causes, symptoms, and treatment helps reduce blame on the individual for the interpersonal strain often caused by ADHD. It also increases partnership in the treatment plan.
What to expect when seeking help
Evaluation
Many psychiatrists and psychiatric nurse practitioners can diagnose and treat ADHD. Minami says good questions to ask any clinical provider from whom you are considering seeking treatment:
- What is your training and experience in treating ADHD?
- What kind of treatments for ADHD do you offer?
- What does an evaluation for ADHD with you entail?
Minami says a comprehensive evaluation for ADHD will include a thorough history of symptoms dating back to childhood, multiple people providing information about the individual, medical and family history, and an assessment for other psychiatric conditions that are either co-occurring or account for the individual’s symptoms that they think are due to ADHD. For example, anxiety and depression often present with symptoms that appear to be due to ADHD, according to Minami. Substance use disorders are also much higher in individuals with ADHD than those without. Significant substance use can be another factor that affects one’s ability to concentrate, organize themselves, and persist through tasks, and needs to be taken into account. The final step of a comprehensive evaluation may include neuropsychological testing.
Medication treatment
Studies show stimulants are the most effective and commonly prescribed medications for ADHD treatment and lead to a significant reduction in symptoms in 70% of adults. Daily medication can reduce interruptive behavior, fidgeting, and other hyperactive symptoms.
Minami says non-stimulants are not as effective in reducing the symptoms of ADHD however, they are helpful in the following circumstances:
- Stimulants didn’t lead to enough reduction of symptoms
- Stimulants are causing side effects that can’t be managed or tolerated (such as weight loss or insomnia)
- Concerning substance use issues
- Individuals have other mental health conditions a particular non-stimulant has shown to help. For example, some are helpful for individuals with co-occurring anxiety, tics, or depression.
Psychotherapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a goal-oriented form of psychotherapy that aims to change negative thinking patterns and change how a patient feels about themself, their abilities, and their future. Minami says CBT is effective for addressing the issues of self-esteem, anxiety, and depression that accompany ADHD.
“ADHD is a very treatable condition,” Minami says. “Receiving a diagnosis can be life-changing, as it can provide clarity and peace of mind. It's a step towards understanding and managing symptoms effectively, and it can open a range of treatment options. A diagnosis of ADHD can be the first step towards a more fulfilling and productive life.”
May is Mental Health Month. Loma Linda University Behavioral Health leads the region in mental health treatment offering the full spectrum of behavioral health programs and services to fit your needs, in Redlands, Murrieta, and Rancho Cucamonga. Click here to request more information about the mental health programs offered.