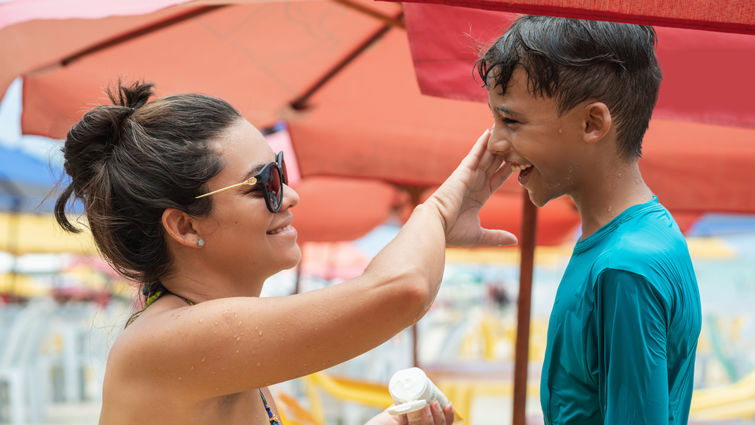
Protecting children from harmful UV rays is essential as families head outdoors to enjoy the summer season. Allison Hensley, MD, a general pediatrician at Loma Linda University Children's Hospital, highlights the risks associated with excessive sun exposure and offers valuable insights into preventative measures parents can take to safeguard their children's skin.
"Children who spend a lot of time outdoors are particularly vulnerable to the damaging effects of the sun's rays," says Hensley. "With a lifetime of sun exposure ahead of them, prioritizing their protection now is crucial."
Hensley explains that while immediate consequences to too much sun include painful sunburns, the long-term effects can be much more severe. Skin cancer remains the primary concern of excessive sun exposure.
"Seek shaded areas, wear broad-brimmed hats to protect the face, and utilize sunglasses for eye protection,’ says Hensley. “Parents should dress their children in protective clothing, including Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) proof clothing, long-sleeved shirts, and long pants, especially during prolonged sun exposure. Last but not least, use sunscreen."
When choosing sunscreen for children, Dr. Hensley advises parents to look for products with a minimum sun protection factor (SPF) of 30. Most studies indicate that SPF 15 is sufficient, but SPF ranging from 15 to 50 are commonly available for children. Broad-spectrum sunscreens that shield against both UVA and UVB rays are essential for comprehensive protection.
Regarding sunscreen ingredients, Hensley recommends zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, especially for children, as these ingredients are less likely to irritate and are considered safe for young and sensitive skin.
The frequency of sunscreen application is a critical factor in maintaining protection. Hensley advises parents to apply sunscreen at least 15 to 30 minutes before sun exposure and reapply every three to four hours for extended outdoor activities. If children engage in water activities, reapply sunscreen every two hours.
Timing is another key consideration in UV safety.
"Avoiding sun exposure during the peak hours of 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. when UV rays are strongest. Instead, plan outdoor activities before 10 a.m. or after 4 p.m. Parents should also be aware that UV rays can penetrate through clouds, making sunscreen essential even on cloudy days."
Parents should avoid excessive sunscreen application on infants under six months of age due to potential skin sensitivity. Instead, Hensley advises parents to cover infants with protective clothing, ensuring that only small amounts of sunscreen are applied to exposed areas like the face. For children older than six months, sunscreen can be safely used on all body areas. But keep in mind that some babies and toddlers may still experience skin irritation due to the chemicals in sunscreen.
To learn more about sun protection, talk to a pediatrician.